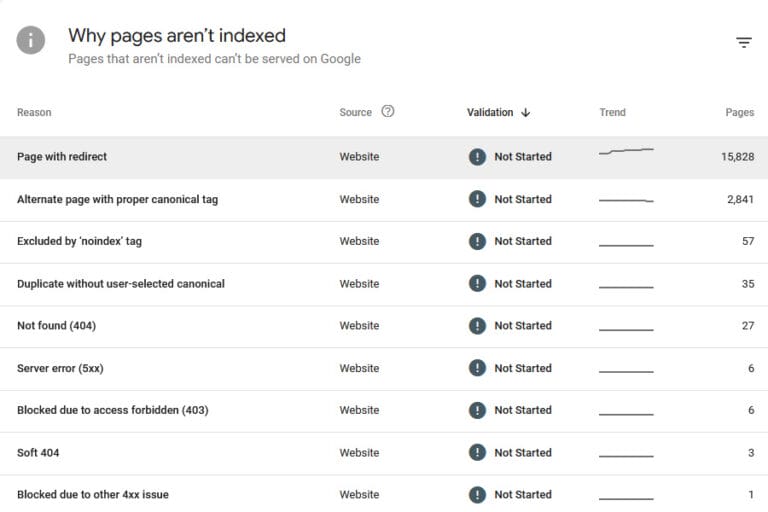
Understanding “Page with Redirect” in Google Search Console
The “Page with Redirect” status in Google Search Console is a significant indicator in the realm of SEO, signaling that certain pages on your website are not being indexed due to redirection. This status can have considerable implications for your site’s SEO performance and overall visibility on the web.
The Mechanics Behind the Status
When this status appears, it means that upon attempting to access a specific page, both users and search engine crawlers are rerouted to a different URL. In response to this redirection, Google index the destination URL rather than the original one. This behavior is integral to Google’s efforts to streamline its indexing process and avoid duplicate content in its search results.
Causes and Implications
- Automatic Redirection: The trigger for this status is an automatic redirection encountered by Googlebot during its crawling process. This can occur for various reasons, from site structure changes to intentional redirection for content consolidation or site migration.
- Impact on Keyword Visibility: When a page that is crucial for certain keywords gets redirected, it can affect the visibility of those keywords in search results. This is particularly relevant if the redirected URL doesn’t align closely with the original page’s content or intent.
- Sitemap Considerations: If the redirected URLs are listed in your sitemap as pages to be indexed, their redirection can lead to a mismatch between your sitemap’s intent and the actual site content accessible to Googlebot. This discrepancy can affect how Google views the accuracy and reliability of your sitemap, which, in turn, can impact your site’s overall SEO performance.
Navigating the “Page with Redirect” Status
- Monitoring: Regularly monitor your site’s Google Search Console reports for the “Page with Redirect” status. Quick detection and resolution can minimize any potential negative impacts on your site’s search performance.
- Analysis: Analyze the redirected pages to understand why they are being redirected. Is it due to a recent site structure change, content consolidation, or a migration to a new domain or protocol (like HTTP to HTTPS)?
- Corrective Actions: If the redirection is unintentional or incorrect, take steps to rectify it. This might involve updating your website’s internal links, modifying your .htaccess file (for Apache servers), or adjusting settings in your CMS.
- Sitemap Updates: Ensure that your sitemap is regularly updated to reflect the current structure of your site. Remove URLs that are no longer relevant or that consistently result in redirection.
- SEO Strategy Alignment: Consider how these redirects align with your overall SEO strategy. Sometimes, redirects are necessary and beneficial from an SEO perspective, such as when dealing with duplicate content or migrating to a more secure, SEO-friendly URL structure.
Understanding and effectively managing the “Page with Redirect” status in Google Search Console is crucial for maintaining a healthy, SEO-optimized website. By closely monitoring and responding to these redirects, you can ensure that your site remains aligned with Google’s indexing guidelines and performs optimally in search results.
Addressing “Page with Redirect” Issues in Google Search Console
Navigating the “Page with Redirect” issue in Google Search Console requires a systematic approach to maintain your site’s SEO health and content visibility. Here’s a detailed guide on how to address and resolve these issues:
Steps to Address “Page with Redirect” Issues
- Identifying Redirected URLs:
- How-To: To access Google Search Console, navigate to the ‘Index’ section and then to ‘Pages.’ Here, you’ll find a list of pages marked with redirects.
- Purpose: This step helps pinpoint exactly which pages are being redirected, allowing you to focus on these specific URLs.
- Inspecting URLs:
- Tool Utilization: Use the URL Inspection Tool in GSC to analyze each redirected URL in-depth.
- Benefits: This tool provides insights into how Google views your page, including whether the page is indexed and any detected issues.
- Checking Redirect Type:
- Tools for Analysis: Employ tools like Redirect Checker or HTTP Status to determine the type of redirect (301 permanent or 302 temporary).
- Significance: Understanding the type of redirect is crucial as it affects how search engines interpret the permanence of the redirect and thus, its impact on your SEO.
- Rectifying Faulty Redirects:
- Action Steps: Adjust or remove inappropriate or no longer necessary redirects.
- Objective: Ensuring that redirects are correctly implemented is vital for proper indexing and maintaining the flow of link equity throughout your site.
Preventing Redirect Issues
- Regular Audits: Conduct periodic checks of your redirect setup. This includes verifying that all redirects are intentional, necessary, and correctly implemented.
- Monitoring Indexing Status: Use GSC to monitor the indexing status of your key pages. This proactive approach allows you to identify and rectify issues as they arise quickly.
A Closer Look at Redirects
Redirects are fundamental to website navigation and SEO. Understanding their mechanics and types is crucial for proper website management:
- Server-Side Redirects:
- Functionality: They automatically forward visitors to a new URL without any action required on the visitor’s part.
- SEO Impact: When Googlebot encounters a server-side redirect, it typically follows to the new URL, indexing the target page instead of the original. This is efficient but requires careful management to avoid losing SEO value from the original page.
Normalcy of “Page with Redirect” Status
- When It’s Expected:
- Website Migration: For example, moving from HTTP to HTTPS, where redirects are necessary to guide users and search engines to the secure version of your site.
- Handling Duplicate Content: Redirecting multiple similar pages to a single, canonical version helps avoid duplicate content issues.
- Temporary Changes: Such as redirecting product pages to an alternative page during out-of-stock periods.
- SEO Considerations:
- Preserving Link Equity: Permanent redirects (301) are typically used to preserve link equity when pages are permanently moved or deleted.
- Temporary Situations: A 302 redirect is appropriate for temporary situations, signaling to search engines that the original page should remain indexed.
Not all cases of this status indicate a problem. It’s normal for pages you no longer wish to display, as their content is better suited on other pages. Common examples include website migrations (like moving from HTTP to HTTPS) and optimizing duplicate content.
When “Page with Redirect” Becomes Problematic
While redirects are a normal part of website maintenance and optimization, they can sometimes lead to significant SEO issues, especially when not implemented correctly or monitored regularly.
Common Redirect Problems
- Mistaken or Messy Redirects:
- Issue: Redirects set up incorrectly or unnecessarily can disrupt the user experience and confuse search engine crawlers.
- Example: A product page that should be directly accessible might be mistakenly redirected to a less relevant page, causing potential loss of traffic and conversions.
- Misinterpretation of Temporary Redirects:
- Issue: Over time, Google might treat 302 temporary redirects as 301 permanent redirects, which can result in the original page being dropped from the index.
- Consequence: This can lead to ranking loss for keywords that the original page was optimized for, and in some cases, can completely remove the page from search results.
Resolving Redirect Issues
Addressing redirect issues requires a systematic approach to ensure long-term website health and search performance.
- Audit for Faulty Redirects:
- Process: Regularly review your redirects in Google Search Console, particularly for pages listed in your sitemap.
- Goal: Identify any redirects that may negatively impact your site’s SEO and rectify them.
- Tools for Examining Redirects:
- Utility: Use online tools to analyze where your redirects are leading and whether they are 301 (permanent) or 302 (temporary).
- Benefit: These tools can help you understand the nature of your redirects and their potential impact on your site’s indexing and SEO.
- Immediate and Long-Term Solutions:
- Short-Term: Quickly remove or correct any inappropriate or unnecessary redirects.
- Long-Term: Conduct a comprehensive technical SEO audit to identify systemic issues that may be causing redirect problems and develop strategies to prevent them.
Next Steps for Optimizing Redirects
- Seek Expert SEO Guidance:
- Advantage: Professional SEO experts can provide detailed insights and tailored solutions for managing redirects and overall SEO health.
- Outcome: Improved site structure, better user experience, and enhanced search engine visibility.
- Undertake a Technical SEO Audit:
- Purpose: To uncover deeper issues contributing to the “Page with Redirect” status.
- Result: A clear roadmap for optimal indexing coverage and enhanced website performance.
Key Takeaways
- Indexing and Redirects: Google typically does not index pages that lead to other URLs via redirects.
- Normal vs. Problematic: While having pages with redirects is often normal, issues arise when these redirects involve key pages or are misinterpreted by Google as permanent.
- Strategic SEO Management: A combination of immediate corrective actions and long-term strategic planning, including regular audits and expert consultations, is vital for resolving redirect issues effectively and maintaining a healthy, high-performing website in the search ecosystem.
The post Understanding “Page with Redirect” Status appeared first on PCM AGENCY.